Now Reading: Binaural Beats Explained: How Two Frequencies Affect the Brain
- 01
Binaural Beats Explained: How Two Frequencies Affect the Brain
Binaural Beats Explained: How Two Frequencies Affect the Brain

🧠 Binaural beats explained simply: two tones, one brain response.
When two slightly different sound frequencies are presented separately to each ear, the brain perceives a third rhythmic pulse. This phenomenon is known as binaural beats—and it reflects how the brain processes timing and frequency differences.
🎧 What Are Binaural Beats?
Binaural beats occur when:
One frequency is played in the left ear
A slightly different frequency is played in the right ear
The brain detects the difference and synchronizes to it
For example, 200 Hz in one ear and 208 Hz in the other may produce an 8 Hz perceived beat—commonly associated with alpha activity.
⚡ How Binaural Beats Affect Brainwaves
Binaural beats don’t force the brain. Instead, they encourage the brain to align with the perceived rhythm.
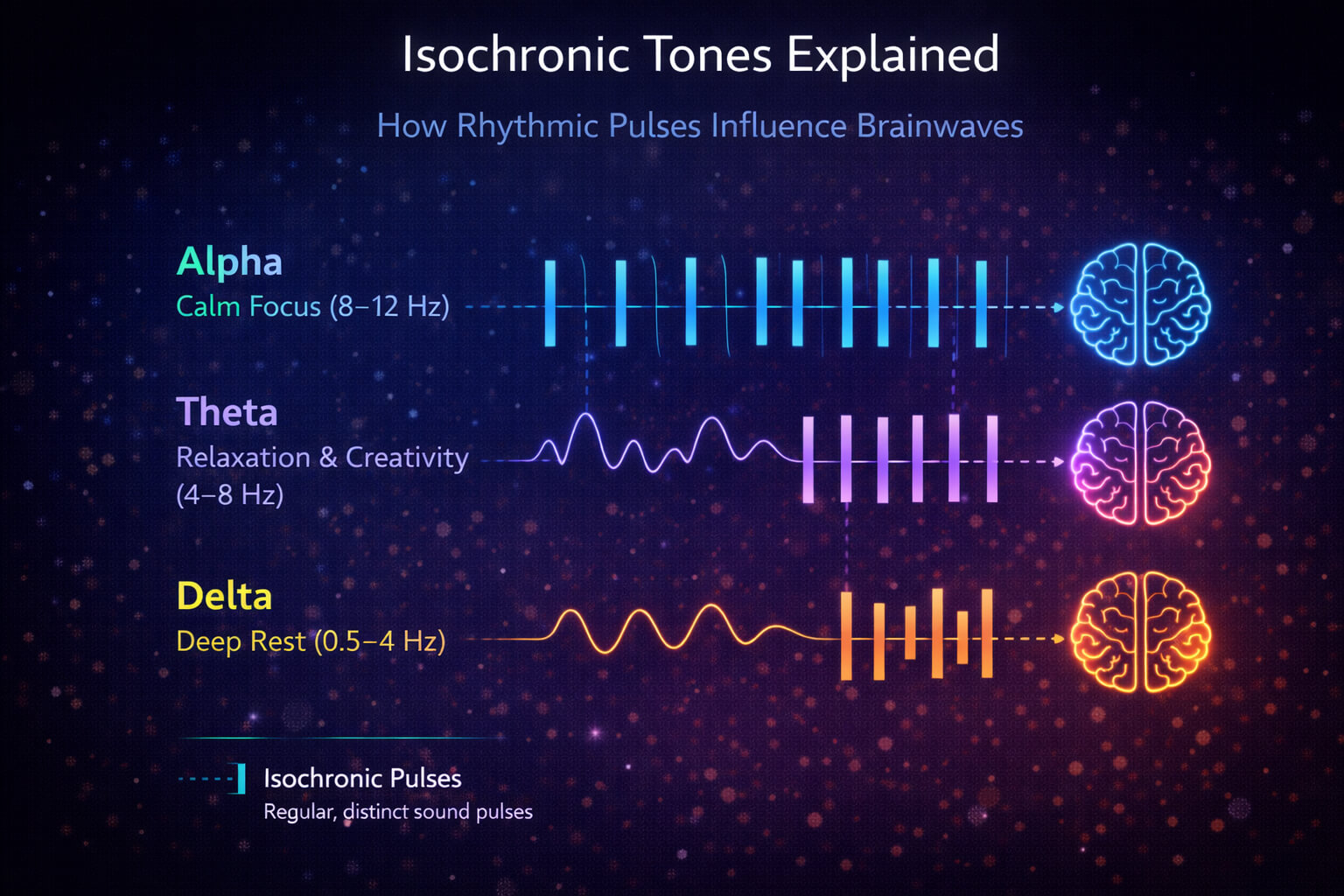
Depending on the frequency difference, binaural beats may support:
Alpha (calm focus)
Theta (relaxation and creativity)
Delta (deep rest)
The effect relies on the brain’s natural timing mechanisms.
📚 Scientific Insight
A review published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience discusses how binaural beats can influence neural oscillations and cognitive states.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00254/full
🧠 Do Binaural Beats Really Work?
Scientific findings suggest effects can vary depending on:
Frequency range
Listening duration
Individual sensitivity
Listening environment
According to research indexed by the NIH, binaural beats may influence attention, mood, and perception when used under appropriate conditions.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4428073/
⚖️ Binaural Beats vs Other Audio Techniques
Unlike isochronic tones or rhythmic music, binaural beats:
Require stereo headphones
Rely on auditory processing inside the brain
Produce a perceived internal rhythm rather than an external pulse
Each method works differently, but all aim to support natural neural synchronization.
🧠 Final Thoughts
Binaural beats explained through neuroscience reveal a simple idea: the brain responds to rhythm.
When sound frequencies are carefully aligned, the brain may follow—shifting attention, calming the mind, or supporting deeper states naturally.
It’s not about forcing change, but guiding it.
👉 Related read: The Science Behind Isochronic Tones: How Sound Shapes the Brain’s Focus for more insights on brainwave focus and mental clarity.