Now Reading: Which Waves Help You Sleep? The Complete Sleep Frequency Guide
- 01
Which Waves Help You Sleep? The Complete Sleep Frequency Guide
Which Waves Help You Sleep? The Complete Sleep Frequency Guide

Sleep isn’t just about rest — it’s a carefully structured neurological process driven by specific brainwave patterns.
If you’ve ever struggled to fall asleep, stay asleep, or wake up refreshed, the real issue may be that your brain isn’t entering the correct frequency states.
Let’s break down exactly which brain waves control sleep and how sound-based entrainment can help.
Understanding the Brain’s Sleep Architecture
Your brain cycles through multiple stages every night, each associated with different frequencies:
Light sleep
Deep sleep
REM sleep
Each stage plays a unique role in physical recovery, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation.
When these stages are disrupted, sleep quality collapses — even if total sleep time seems “normal.”
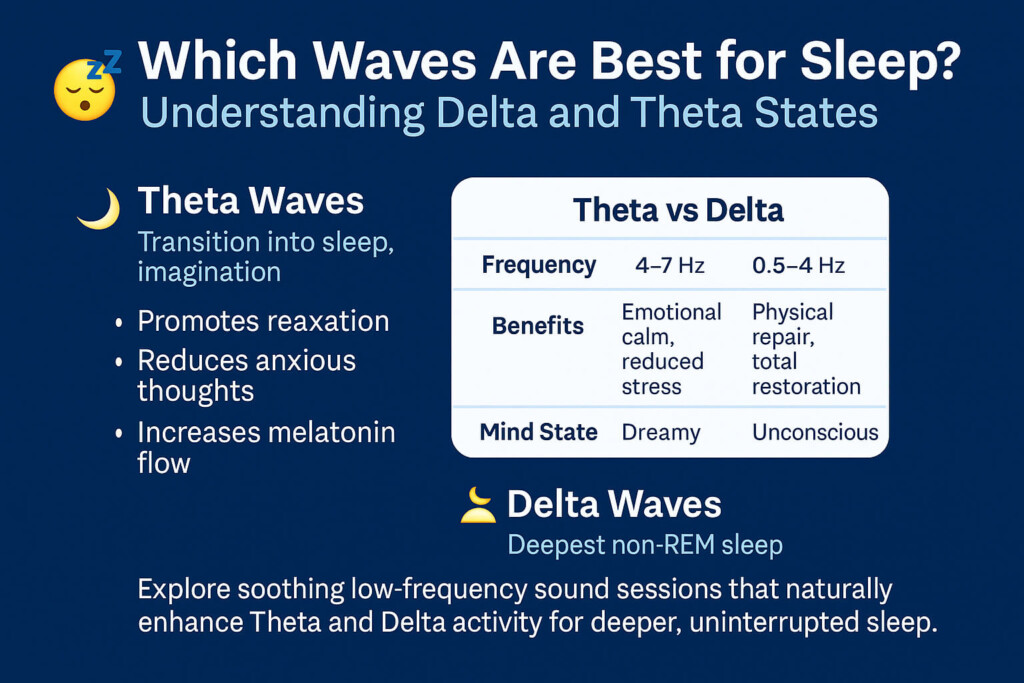
Delta Waves (0.5–4 Hz): Deep Sleep & Physical Repair
Delta waves dominate the deepest stages of sleep.
This is when your body does the heavy lifting:
Tissue repair and muscle recovery
Immune system strengthening
Growth hormone release
People lacking Delta activity often report waking up tired despite long sleep durations.
Theta Waves (4–7 Hz): Falling Asleep & Dream States
Theta waves act as the gateway between waking consciousness and sleep.
They are associated with:
Rapid sleep onset
Hypnagogic imagery (pre-dream visuals)
Emotional processing
If your mind races at night, Theta activity is usually insufficient or unstable.
Sound entrainment at Theta frequencies helps quiet analytical thinking and ease the transition into sleep.
REM Sleep & Mixed Frequencies
REM sleep doesn’t belong to a single wave category.
Instead, it involves a dynamic mix of Theta and faster frequencies.
This stage is essential for:
Memory integration
Emotional balance
Learning consolidation
Disrupting REM sleep can lead to irritability, poor focus, and mood instability the next day.
Why Sound Frequencies Work for Sleep
Unlike medication, frequency-based audio doesn’t suppress the brain — it guides it.
Brainwave entrainment works by gently synchronizing neural activity with external rhythmic stimuli, allowing the brain to follow its natural sleep architecture.
How to Use Sleep Frequencies Correctly
For best results:
Use stereo headphones or low-volume speakers
Start sessions 20–30 minutes before sleep
Avoid screens during listening
Keep volume low — clarity matters more than loudness
Consistency matters more than duration.
Sleep is trained, not forced.
Final Thoughts
So, which waves help you sleep?
Delta restores the body
Theta calms the mind
Balanced transitions preserve REM cycles
When these frequencies work together, sleep becomes effortless instead of frustrating.
Sound won’t replace healthy habits — but it can teach your brain how to rest properly again.
👉 Related read: Surprising Benefits of Gamma Brain Waves for more insights on brainwave focus and mental clarity.